Abstract
Introduction: Daratumumab (DARA)-based regimens are effective and well tolerated in both newly diagnosed and relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) patients. However, the prognosis for patients who have become refractory to proteasome inhibitors (PIs), immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) and DARA is poor. A better understanding of determinants of response and mechanisms of resistance to DARA may lead to new rationally designed treatment strategies. We therefore characterized the effect of DARA on the immune system in MM patients treated with DARA monotherapy in part A of the DARA-ATRA study (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02751255).
Methods: In part A of this prospective multicenter phase 2 trial, 63 DARA-naïve patients were treated with DARA monotherapy (16 mg/kg; approved schedule). Median number of prior lines of treatment was 4 (range 2-11), all patients were previously exposed to lenalidomide and a PI; 89% was refractory to an IMiD, 71% to a PI and 67% to both IMiD and PI.
Bone marrow (BM) aspirates obtained at baseline (BL) and at progression (PD; primary refractory, or acquired resistance after prior response) were subjected to deep immune profiling using 28 surface- and intracellular proteins measured by flow cytometry (BL n=51, PD n=47). In a subset of these patients (BL n=39, PD n=33) mass cytometry (CyTOF) was also performed profiling 39 proteins. In addition, peripheral blood (PB) samples obtained at BL (n=44) and PD (n=37) were analyzed using CyTOF.
Computational analyses of flow data were performed using UMAP and FlowSOM; CyTOF data were analyzed using SPADE and Freeviz. Statistical analyses included Wilcoxon rank-sum and signed-rank tests, Generalized Linear Mixed Models and ANOVA.
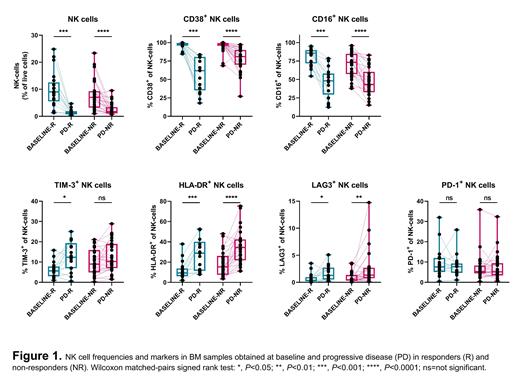
Results: A partial response or better was achieved in 41% of patients treated with DARA monotherapy. We compared immune profiles of responding and non-responding (primary-refractory) patients. At BL, the percentages of MM-, T-, B- and NK cells in BM were similar between both groups. However, NK cells of non-responding patients had a lower proportion of CD16 + (P=0.029), and a higher proportion of TIM-3 + (P=0.010) and HLA-DR + (P=0.043) NK cells, suggesting an exhausted phenotype. Non-responders also had a higher proportion of TIM-3 + CD4 + (P=0.022) and TIM-3 + CD8 + T-cells (P=0.004), and a higher proportion of TIM-3 + regulatory T-cells (Tregs) (P=0.042).
A higher proportion of TIM-3 + -NK cells, -T-cells, or -Tregs in BM was also associated with poor progression-free and overall survival (PFS; OS). In addition, clinical characteristics associated with poor PFS such as LDH (P=0.016), extramedullary disease (P=0.001) and (R-)ISS stage III (P=0.015) were associated with an increased number of phenotypically exhausted NK- and T-cells.
Similar to prior studies, DARA treatment resulted in reduced levels of CD38 on all immune cell subsets and a marked decrease in Tregs, regulatory B cells (Bregs) and NK cells in both BM and PB. Upon acquired resistance, remaining NK cells displayed higher proportions of TIM-3 + (P=0.022), HLA-DR + (P=0.0007) and LAG-3 + (P=0.011), and lower proportions of CD16 + (P=0.002) (Figure 1), compatible with an exhausted phenotype. Furthermore, disease progression was associated with an increase in CD4 + and CD8 + terminally differentiated effector memory T-cells and a decrease in CD4 + and CD8 + central memory T-cells in BM. There was no significant change in the proportion of T-cells expressing immune checkpoint molecules.
CyTOF analysis of BM and PB samples confirmed flow cytometric findings. Furthermore, data-driven analysis identified immune profiles specific to progression, including a significant decrease in the fraction of Granzyme B + NK cells, and increase in the fraction of Granzyme B + Bregs at the time of progression.
Based on NK cell depletion and -exhaustion observed at PD, we hypothesized that NK cell repletion may restore DARA sensitivity. Indeed, in ex vivo experiments we show that DARA-resistance can be overcome by addition of healthy donor derived NK cells to MM cells obtained from DARA-refractory patients.
Conclusion: Here we show that an increased proportion of NK cells with an exhausted phenotype is associated with primary and acquired DARA-resistance, which is in line with the important role of NK cells in DARA-mediated tumor cell elimination ex vivo. Future DARA-based treatment strategies may benefit from reinvigorating NK cells and restoring their cytotoxic capacities.
Zweegman: Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BMS: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Oncopeptides: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Minnema: Celgene: Other: Travel expenses; Alnylam: Consultancy; Cilag: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Kite/Gilead: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy. Broyl: Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Levin: Roche, Janssen, Abbvie: Other: Travel Expenses, Ad-Board. Kersten: Kite/Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Takeda: Consultancy; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy; Miltenyi Biotech: Consultancy. Krevvata: Janssen: Current Employment. Casneuf: Janssen: Current Employment. Abraham: Janssen: Current Employment. Verona: Janssen: Current Employment. Smets: Janssen: Current Employment. Vanhoof: Janssen: Current Employment. Cortes-Selva: Janssen: Current Employment. van Steenbergen: Biolizard working for Janssen: Current Employment. Vieyra: Janssen: Current Employment. Sonneveld: Karyopharm: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; SkylineDx: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Mutis: Janssen: Honoraria; Genmab: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; ONK Therapeutics: Research Funding. van de Donk: Adaptive Biotechnologies: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Cellectis: Research Funding; Servier: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal